Install Git on Mac OS X
- For compatibility, Linux binaries are built with CentOS 6.4 i386/amd64. Only 64-bit is supported. IOS development requires the latest Xcode.
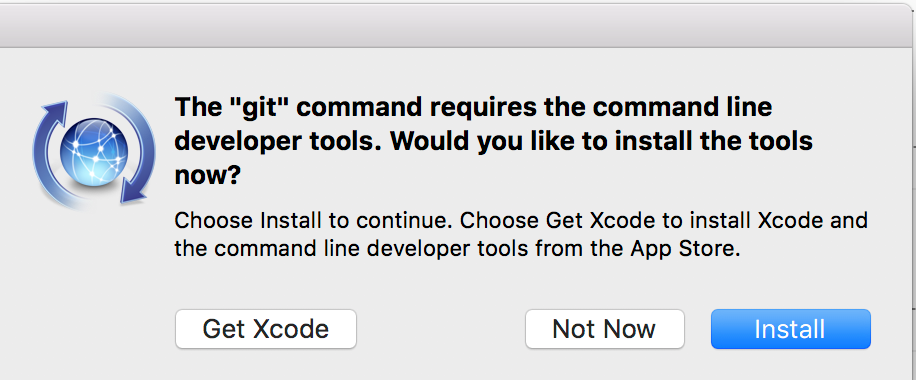
- The first step for Python 3 is to install Apple’s Xcode program which is necessary for iOS development as well as most programming tasks. We will use XCode to install Homebrew. In your Terminal app, run the following command to install XCode and its command-line tools: $.
- Install Git on Mac OS X There are several ways to install Git on a Mac. In fact, if you've installed XCode (or it's Command Line Tools), Git may already be installed.
Xcode menu Preferences Downloads choose 'Command line tools' Click 'Install' button: Fig.02: Installing gcc compiler on Mac OS X Xcode will download package and install copies of the core command line tools and system headers into system folders, including the LLVM compiler, linker, and build tools. Install-LaTeX-Guide-zh-cn (A short introduction to LaTeX installation written in Chinese) This package will introduce the operations related to installing TeX Live (introducing MacTeX in macOS), upgrading packages, and compiling simple documents on Windows 10, Ubuntu 20.04, and macOS systems, and mainly introducing command line operations.
There are several ways to install Git on a Mac. In fact, if you've installed XCode (or it's Command Line Tools), Git may already be installed. To find out, open a terminal and enter git --version.
Apple actually maintain and ship their own fork of Git, but it tends to lag behind mainstream Git by several major versions. You may want to install a newer version of Git using one of the methods below:
Git for Mac Installer
The easiest way to install Git on a Mac is via the stand-alone installer:
Download the latest Git for Mac installer.
Follow the prompts to install Git.
Open a terminal and verify the installation was successful by typing
git --version:Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
(Optional) To make Git remember your username and password when working with HTTPS repositories, configure the git-credential-osxkeychain helper.
Install Git with Homebrew
If you have installed Homebrew to manage packages on OS X, you can follow these instructions to install Git:
Open your terminal and install Git using Homebrew:
Verify the installation was successful by typing which
git --version:Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
(Optional) To make Git remember your username and password when working with HTTPS repositories, install the git-credential-osxkeychain helper.
Install Git with MacPorts
If you have installed MacPorts to manage packages on OS X, you can follow these instructions to install Git:
Open your terminal and update MacPorts:
Search for the latest available Git ports and variants:
Install Git with bash completion, the OS X keychain helper, and the docs:
Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
(Optional) To make Git remember your username and password when working with HTTPS repositories, configure the git-credential-osxkeychain helper.
Install the git-credential-osxkeychain helper
Bitbucket supports pushing and pulling your Git repositories over both SSH and HTTPS. To work with a private repository over HTTPS, you must supply a username and password each time you push or pull. The git-credential-osxkeychain helper allows you to cache your username and password in the OSX keychain, so you don't have to retype it each time.
If you followed the MacPorts or Homebrew instructions above, the helper should already be installed. Otherwise you'll need to download and install it. Open a terminal window and check:
If you receive a usage statement, skip to step 4. If the helper is not installed, go to step 2.
Use curl to download git-credential-osxkeychain (or download it via your browser) and move it to
/usr/local/bin:Make the file an executable:
Configure git to use the osxkeychain credential helper.
The next time Git prompts you for a username and password, it will cache them in your keychain for future use.
Install Git with Atlassian Sourcetree

Sourcetree, a free visual Git client for Mac, comes with its own bundled version of Git. You can download Sourcetree here.
To learn how to use Git with Sourcetree (and how to host your Git repositories on Bitbucket) you can follow our comprehensive Git tutorial with Bitbucket and Sourcetree.
Build Git from source on OS X
Building Git can be a little tricky on Mac due to certain libraries moving around between OS X releases. On El Capitan (OS X 10.11), follow these instructions to build Git:
From your terminal install XCode's Command Line Tools (if you haven't already):
Install Homebrew.
Using Homebrew, install openssl:
Clone the Git source (or if you don't yet have a version of Git installed, download and extract it):
To build Git run make with the following flags:
Install Git on Windows
Git for Windows stand-alone installer
Download the latest Git for Windows installer.
When you've successfully started the installer, you should see the Git Setup wizard screen. Follow the Next and Finish prompts to complete the installation. The default options are pretty sensible for most users.
Open a Command Prompt (or Git Bash if during installation you elected not to use Git from the Windows Command Prompt).
Run the following commands to configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
Optional: Install the Git credential helper on Windows
Bitbucket supports pushing and pulling over HTTP to your remote Git repositories on Bitbucket. Every time you interact with the remote repository, you must supply a username/password combination. You can store these credentials, instead of supplying the combination every time, with the Git Credential Manager for Windows.
Install Git with Atlassian Sourcetree
Sourcetree, a free visual Git client for Windows, comes with its own bundled version of Git. You can download Sourcetree here.
To learn how to use Git with Sourcetree (and how to host your Git repositories on Bitbucket) you can follow our comprehensive Git tutorial with Bitbucket and Sourcetree.
Install Git on Linux
Debian / Ubuntu (apt-get)
Git packages are available via apt:
From your shell, install Git using apt-get:
Verify the installation was successful by typing
git --version:Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
Fedora (dnf/yum)
Git packages are available via both yum and dnf:
From your shell, install Git using dnf (or yum, on older versions of Fedora):
or
Verify the installation was successful by typing
git --version:Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma's name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create
Build Git from source on Linux
Debian / Ubuntu
Git requires the several dependencies to build on Linux. These are available via apt:
From your shell, install the necessary dependencies using apt-get:
Clone the Git source (or if you don't yet have a version of Git installed, download and extract it):
To build Git and install it under
/usr, runmake:
Fedora
Git requires the several dependencies to build on Linux. These are available via both yum and dnf:
From your shell, install the necessary build dependencies using dnf (or yum, on older versions of Fedora):
or using yum. For yum, you may need to install the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository first:
Symlink docbook2X to the filename that the Git build expects:
Clone the Git source (or if you don't yet have a version of Git installed, download and extract it):
To build Git and install it under
/usr, runmake:
Install Latest Xcode Install
Next up:
Setting up a repository
Start next tutorialHistorically MacOS came preinstalled with Python 2, however starting with Mac 10.15 (released in October 2019) this is no longer the case. And since Python 2 will no longer be officially supported as of January 1, 2020, you should really use Python 3 instead.
There are multiple ways to install Python 3 on a MacOS computer. The official Python website even recommends downloading it directly, however this approach can cause confusion around PATH variables, updates, and uninstalls. A better approach, in my opinion, is to instead use the popular package manager Homebrew which automates updates and juggling multiple versions of Python on a computer.
Is Python 3 already installed?
Before we start, make sure Python 3 isn’t already installed on your computer. Open up the command line via the Terminal application which is located at Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal.
Then type the command python --version followed by the Enter key to see the currently installed version of Python.
Note: The dollar sign, ($), indicates user input. Everything after is intended to be typed by the user followed by the Enter key. Any output, such as Python 2.7.17 in this case, does not have a dollar sign in front.In short: don’t type $ before your commands!
It’s possible that Python 3 may have already been installed as python3. Run the command python3 --version to check, however most likely this will throw an error.
Install XCode
The first step for Python 3 is to install Apple’s Xcode program which is necessary for iOS development as well as most programming tasks. We will use XCode to install Homebrew.
In your Terminal app, run the following command to install XCode and its command-line tools:
It is a large program so this make take a while to download. Make sure to click through all the confirmation prompts XCode requires.
Install Homebrew
Next install Homebrew by copy/pasting the following command into Terminal and then type Enter:
To confirm Homebrew installed correctly, run this command:
Install Python 3
Now we can install the latest version of Python 3. Type the following command into Terminal and press Enter:
To confirm which version of Python 3 was installed, run the following command in Terminal:
Finally, to run our new version of Python 3 open an interactive shall by typing python3 within Terminal:
To exit the Python 3 interactive shell, you can type either exit() and then Return or type Control+d which means hold both the Control and D keys at the same time.
Note that it is still possible to run Python 2 by simply typing python:
Virtual Environments
By default, Python packages are installed globally on your computer in a single directory. This can cause major problems when working on multiple Python projects!
For example, imagine you have Project A that relies upon Django 1.11 whereas Project B uses Django 2.2. If you naively installed Django on your computer, only the latest install would be present and available in that single directory. Then consider that most Python projects rely on multiple packages that each have their own version numbers. There’s simply no way to keep everything straight and not inadvertently break things with the wrong package versions.
The solution is to use a virtual environment for each project, an isolated directory, rather than installing Python packages globally.
Confusingly, there are multiple tools for virtual environments in Python:
- venv is available by default on Python 3.3+
- virtualenv must be installed separately but supports Python 2.7+ and Python 3.3+
- Pipenv is a higher-level tool that automatically manages a separate virtual environment for each project
On MacOS we can install Pipenv with Homebrew.
Then use Pipenv for any Python packages you wish to install. For example, if you want to work with Django 2.2.6, first create a dedicated directory for it on your computer such as in a django directory on your Desktop.
Then install Django within that directory.
Install Latest Xcode Version
If you look within the directory there are now two new files, Pipfile and Pipfile.lock, which Pipenv uses. To activate the virtual environment type pipenv shell.
There will now be parentheses around the name of your current directory which indicates the virtual environment is activate. To exit the virtual environment, type exit.
The lack of parentheses confirms the virtual environment is no longer active.
Next Steps
To learn more about Python, the books Python Crash Course and Automate the Boring Stuff are great resources. For free tutorials on web development with Python check out Learn Django.
